Full Guide to Successfully Pivot Your SaaS Startup
The term pivot came from ballroom dancing. How he migrated is unknown, but physically it means the rotation of partners clockwise or counterclockwise, pressed close to each other. In startups, the meaning is slightly different. If your current business model is unprofitable or not profitable enough for you to develop, you need a pivot.
We have already mentioned pivots in the article Development costs growth on a post MVP phase of a SaaS product and today we will talk about how to pivot in a saas startup, which can be a turning point in the life of a project, and how to understand that it's time to change course and look at the problem that your tech startup is solving from a new angle.
What Is A Pivot in Startup?
If you wonder what is meant by pivot for a startup, it is a change in the course of movement of a startup in order to test a new direction of development. Pivot can test a fundamental hypothesis about a product, business model, or growth engine. For example, Flickr was conceived as an image-saving tool for the online game Game Neverending, but in the end, the creators closed its development and focused only on the photo gallery function. Startup pivot enters the stages of startup development proposed in the lean startup methodology of Eric Ries.
If we make this sharp turn early, when we are still finishing the idea, this is not a pivot, but an iteration of the idea. The analogy from dancing still takes place. If the team is cohesive enough, then we will not scatter in different directions and will remain in the same composition.
A classic pivot is a Slack case - after creating the Glitch game, the guys turned 360 degrees and wrote down a corporate messenger. All they took from the game was a messaging tool.
Reasons You Need to Pivot Your SaaS Startup
For investors, the speed of development is the only reliable indicator that a startup can take off. It is better to immediately realize that the idea is bullshit and without regret to move on to another than to have hints of traction.
Traction * is the “grip” of our product with the market. Revenue or the number of active users can be used as indicators. This is proof that we are in demand. But this is not yet a product-market fit. So what is the sign that you were doing it all wrong?
The startup doesn't solve the user problem
The target audience you are targeting is not interested in your proposal, since it solves a problem that is not important to them. You need to reach out to an audience for which your solution will be of value, or identify a problem with your current audience and solve it (see customer segment pivot and customer needs).
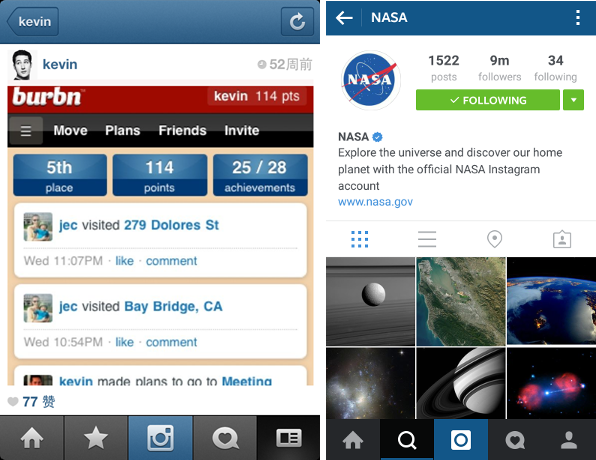
Successful startups do not hide the fact that they had to go through a pivot. For example, the startup company Instagram was originally called Burbn and offered too many functions (check-ins, scheduling them, and taking photos from meetings with friends). It turned out that the check-ins component is not interesting to users, but they are happy to use the ability to quickly share photos. Its creators used this information to launch a startup that Facebook acquired for $ 1 billion in 2012.
The startup is failing to attract the right users
This situation can arise if you neglected the opportunity to create an MVP or simply because the target audience turned out to be smaller than expected. In this case, you will need to expand your audience or reorient to a new one (see pivot segment of consumers and business architecture).
User acquisition or retention strategy does not generate enough startup growth
Your Internet startup solves the user problem, but the channel you use to attract is ineffective. Either the cost of attracting one user or CAC (Customer acquisition cost) is too high. Then you should consider pivoting your monetization method, growth engine, or distribution channel.
Customers are not willing to pay a startup
You offer a solution to an important user problem, but they are in no hurry to pay you. Perhaps the price is too high or doesn't match their idea of the value of the product? You can reduce the price by reducing the number of unused functions and focusing only on 1-2 important features (see pivot increase). And in order to find paying customers, you need to expand the product's capabilities or reorient it to an entirely new audience (see pivot reduction and pivot of business architecture).
It is not for nothing that Uber and Airbnb launched separate services for B2B customers - competition in it is lower because new startups usually offer B2C solutions. That is a great example of a successful startup pivot.
It's too expensive for a startup to make a product
This problem is more common for startups that make physical goods like home electronics, but IT startups have heard of it too. In this case, you need to look for ways to reduce the cost: perhaps you should abandon the support of a large website and provide your services only through the application (see the pivot platform)? Or pivot technology and switch to a less expensive solution?
If your startup faces these hurdles, and the real data doesn't meet the baselines (enrollment, activation, retention, referral, and revenue) established during the planning phase, it's time to make a U-turn and quickly test new assumptions about the direction of the startup. A startup's pivot will help you save money and find a path to sustainable success, as you now have the latest insight into the real needs of users.
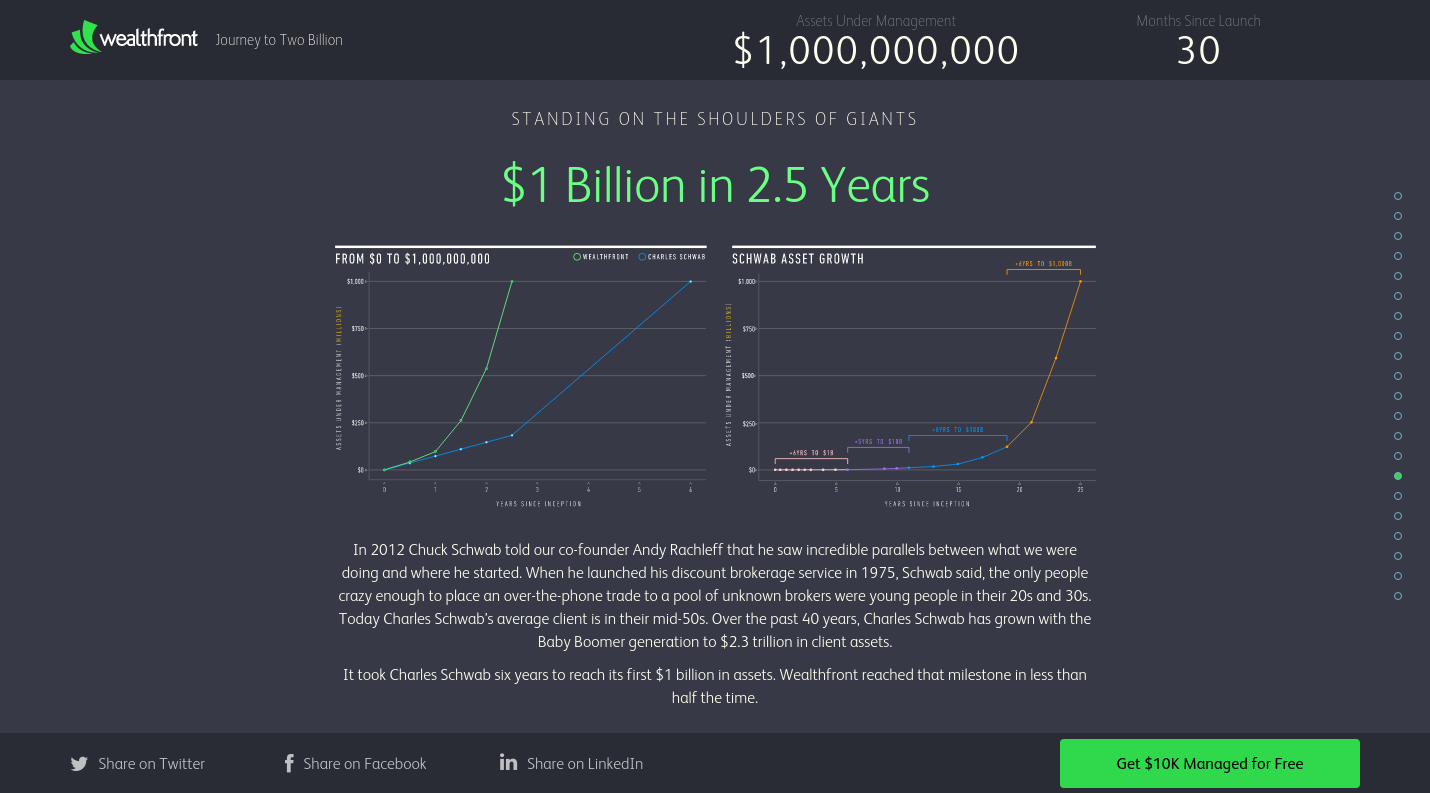
For example, the creation of the startup Wealthfront began with the game kaChing to identify successful hobbyist traders. It turned out that the percentage of such people among the players is negligible. However, the idea caught the attention of professional traders. The start-up pivot has created a successful company that simplifies the investment process for individual clients.
Types of SaaS Pivots
Having identified the reason for the lack of success of the startup among the target audience, you can plan a pivot of one of the following types:
Zoom-in pivot
One of the product functions becomes a separate product. This pivot was made by Votizen when it abandoned the idea of a social network and made a simple service for lobbying the interests of voters. For details on the company's pivot series and other examples of startups, see Lean Startup.
Zoom-out pivot
The original product becomes part of the new multi-functional product. The idea behind the startup Yelp was to create a recommendation email service, but after the pivot, it became a full-fledged portal with reviews and ratings of local companies.
Customer segment pivot
The company sees that it is solving the problem of the wrong customers, which it was initially targeting, and switches to the segment in which its product is in demand. This is what IMVU did: by determining what needed to adapt to a new audience, the company simplified its product according to its needs.
Customer need pivot
It turns out that the problem the product solves is not that important to the target audience, but the data collected shows that there is another problem that the startup can solve. Pinterest was conceived as a replacement for paper shopping catalogs. It turned out that users are more like creating lists of beautiful things and sharing them, so the startup began to develop in this direction.
Platform pivot
Moving from application to platform or vice versa. When startup Cofinity decided to end support for Palm Pilot and focus on the web platform, it made the right decision and grew to a successful company called PayPal.
Value capture pivot
Changing the way of making a profit from (freemium, subscription,% from transactions, selling advertising). It may turn out that startup projects have chosen a monetization model that is not suitable for their product, or the interaction with users was not built correctly, so the model will have to be changed. Steve Blank described such a case in a post for LinkedIn.
Business architecture pivot
According to Jeffrey Moore, companies choose the complex systems model (high-profit margins and low sales) or the volume of operations model (low-profit margins and high sales volumes). In practice, this usually means choosing between B2B and B2C. The competition among B2C solutions like instant messengers is huge, but in the B2B market, enterprise messenger Slack is popular.
The engine of growth pivot a SaaS product
In the event of such a turn, the company chooses the growth mechanism that best suits its goals. Eric Rice identifies three such mechanisms:
- The mechanism of "sticky" growth - attracting and retaining customers for a long time.
- The viral growth mechanism is spread through users who promote the product and thus take over most of the marketing.
- The mechanism of paid growth is to increase the profitability of each paid customer (for example, who clicked on an AdWords advertisement) or to reduce the cost of its acquisition.
Channel pivot
Changing the mechanism by which startup projects deliver their product to customers. For example, in the case of games, this could be switching from the Humble Store to Steam or selling a product through its own website.
Technology pivot
Transfer of existing functionality to new technology while maintaining the existing customer base. This is usually done by already stable companies, for example, Spotify switched to Symfony2.
Step-by-step Guide on How To Pivot a SaaS Startup: The best strategies
When a startup is thinking of pivoting the general focus should both on areas that are going bad and areas where things are going haywire. Customer profiling and market research help in gauging response that is essential for the startup to figure this out.
The major pivot strategies for saas startups to focus on would be :
Technical Development
Focussing on good areas and bad areas require a significant amount of resources and would require hiring to achieve those goals.
Complete revamp should ideally be fast but reliable and therefore spending time while hiring goes a long way and it becomes a make or breaks point after pivoting.
Improvement In Revenue Model
Even if you are well backed up by the technical department, you might need to work on revamping the revenue model for your venture if it is app-based. You might need to take pointers from various revenue models that are in existence and pick out the one that is best suited.
Marketing
If the venture has seen a dip in the popularity then marketing strategies, partnerships with opinion leaders become essential for the enterprise.
Focussing on identifying the areas where work needs to be done helps a startup create a roadmap for the future successfully pivoting a saas business.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, we want to say that you shouldn't think that the pivot strategy for saas is “the beginning of the end”. Well-known startups can go through a series of pivots before finding their niche. Therefore, pivoting SaaS development might be an opportunity, with new knowledge, to deploy a startup project in such a way as to get a constant influx of loyal customers and the greatest profit.
If you feel that you have come to the stage when you need drastic changes pivoting in a saas business, then we have repeatedly gone this way with our projects and are ready to help you with the custom development solution.