IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Understanding the Differences
You can often find abbreviations such as IaaS, PaaS and SaaS in the cloud solutions and services description. Even in our articles and service pages, the phrase "SaaS software development" is constantly used. However, not all of our clients understand the meaning of these terms and their business value. Let's look at the differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS, how they work, and what capabilities they provide to cloud users.
What is IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS?
All of them are cloud computing services, each designed to meet the specific needs of B2B companies.
You, for example, need those cloud business and productivity solutions offered by vendors as SaaS to keep your young company running daily and help it grow.
Other companies, such as those that develop software, may require a cloud-based platform that they can use to create custom apps. There’s PaaS for this.
Others may still need whole cloud infrastructure resources to build and manage their network, servers, apps, operating systems, and data storage. IaaS answers this particular need.
Any of the above services are designed to remove a certain part of the time and financial costs for the deployment and support of your IT service (be it a business card site, a 1C server in the cloud, or a large corporate project). The difference lies in how much of the worries you leave for yourself and what you leave to the service provider's management.
Difference Between Cloud Computing Server Models: Local or IaaS or PaaS or SaaS
|
Model |
Description |
Examples |
|
Local |
Software installed and run locally on the user's computer or server. |
Microsoft Office, Adobe Photoshop |
|
IaaS |
Infrastructure as a Service provides virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, networking, and operating systems. The user can deploy and manage their own applications on these resources. |
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure |
|
PaaS |
Platform as a Service provides a platform for developers to deploy, manage and run their applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. The provider manages the infrastructure, middleware, operating system, and runtime. |
Google App Engine, Heroku |
|
SaaS |
Software as a Service provides a complete software solution that is hosted and managed by the provider. The user accesses the software via a web browser or an API, and the provider takes care of all the underlying infrastructure, security, and maintenance. |
Salesforce, Gmail, Dropbox |
Thus, let us first look at the traditional on-premises world of content management systems. In the pizza world, that translates into doing everything yourself – everything from getting the ingredients together to having the equipment needed to turn those ingredients into a cooked pizza to supplying the dining table and beverages for your complete pizza dinner. If you’re into creating your own home-grown CMS, I suppose you could stretch the analogy to say that you’ve gone to the extreme of growing your tomatoes, milking your cows and kneading your dough.
Think of “Take and Bake” or “Go Get that Frozen Pizza” as an analogy for Infrastructure as a Service. All you need to worry about is the stuff to warm and serve that pizza. In the CMS world, IaaS usually means having the vendor take care of the hardware running the content management system, ensuring the server, storage, load balancers, network, and what-all are at peak performance.
With Platform as a Service, you don’t have to manage the underlying operating hardware or software. In the pizza world, all you need to do is set the table because the pie will be delivered to you ready to eat. The only thing you need to be concerned with in the CMS world is the CMS itself. The infrastructure and platform are taken care of by the vendor.
And finally, we ended up with Software as a Service. Pizza-wise, you’re dining out and enjoying a thin-crust or deep-dish Chicago-style pie. In CMS-land, you can concentrate on content for your website and your marketing initiatives and don’t have to worry about patches, security, and maintenance upgrades.
What Are the End-User Controls in SaaS?
SaaS is a fully configured and ready-to-use program that performs specific functions. The only difference between SaaS technology and software on a smartphone or computer is that the software is in the cloud. It is accessed via the Internet, and the program itself runs on the capacities of virtual servers, so it does not load your computer or smartphone.
In SaaS deployments, the provider manages everything from hardware and software to installation and management of the application. This model is the most affordable and requires few resources and little involvement on the customer’s part. The downside is minimal control over the application’s features and a limited ability to customize the user interface.
Along with factors such as budget, in-house skills and resources, and time to market, the organization’s need for control and complexity will determine which delivery model is the most appropriate for a particular workload or business function. For instance, the SaaS model is often a good fit for generic functions, such as email, with low complexity and customization requirements. Specific business functions that require more control over data and processes are better suited to IaaS deployments, especially in large enterprises with the internal staff and expertise needed to manage and oversee dynamic infrastructure.
SaaS is the end result, allowing businesses to deliver software on-demand to customers. With SaaS, vendors can provide software via the Internet to users and customers. A connected device and browser are all users need to access and use the software.
What is the SaaS Option for Your Business?
SaaS is the most popular option for B2B companies in the cloud computing market because of its many benefits. SaaS businesses offer several benefits to their customers, whether that be for finding a ride, or a song they like, hosting huge amounts of data, or running multiple field agents. There are many benefits to utilizing SaaS for companies, including the reduced upfront costs of commercial software, the need to install software on individual machines, service scalability with a business’s growth, integrations with other software, and instant updates to all users. That are just a few of the benefits. One of the major benefits is that the software never goes out of date, just keeps getting updated.
Set up (if any) and implementation is easy and quick. You’ll be up and running and using the software in no time without the need for IT experience or IT experts. The vendor manages all the technical side – security, storage, servers, middleware and more.
Our last analogy, “travel as a service” likens SaaS to an all-inclusive vacation where the essentials – booking, accommodation, transport, food, etc. – are all taken care of.
When is SaaS Being Utilized?
Companies use an average of 16 SaaS apps daily to run their business. If you’ve used SaaS – personally or professionally – you will see that SaaS is suitable for anyone.
Do you subscribe to Dropbox to store your photographs or docs online? That’s a great example of SaaS!
If you’re a marketer and use an email marketing platform to send emails to your customers, then you most likely use a subscription-based model.
For medium-size organizations in particular, SaaS is primarily a hassle-free and cost-effective alternative that offers new possibilities, flexible costs, and easy maintenance and deployment.
You don’t need to own a super powerful computer, an in-house server or employ an IT genius to be able to store your business information in the Cloud. SaaS allows multiple users to access the vast database anytime and anywhere on the Internet.
All you need is a web browser and an internet-powered device and you’re up and running.
SaaS Advantages
You can clearly see the many advantages of SaaS compared to an on-premise solution. Maintenance and security patches and updates are handled by the vendor and done automatically with no downtime. Mobile versions of the app usually come as part of the software package, allowing you to use the software anytime and anywhere you go. Several tiered pricing plans are also available to fit the company budget and requirements, whether yours is an SMB or a large enterprise. Becoming a de facto offering by vendors are free SaaS tools for small businesses to help jumpstart your company.
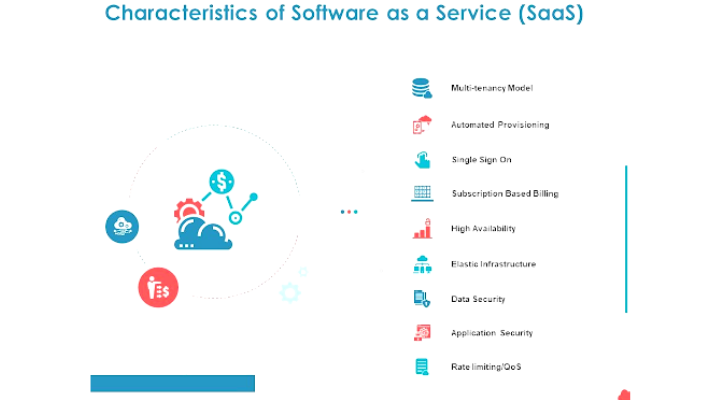
SaaS Characteristics
Examples of SaaS
Examples of SaaS are most Internet services: email, CRM systems, task schedulers, web builders for building sites, and blogging platforms. That is all cloud programs that allow you to solve specific problems.
Let’s take a look at HubSpot. It is one of the most popular cloud-based CRM platforms for growing sales teams and is offered completely free. You get basic features to help your team simplify sales processes. It enables you to manage contacts, company records, meetings, deals, tasks, tickets, documents, and forms. You’ll be able to quickly create, schedule and track emails, and collaborate with colleagues through team email, conversation inbox, and built-in live chat. HubSpot CRM has a huge integration capability, making it compatible with any software ecosystem.
Use Cloud Services and Protect the Future of Your Business
We developed and polished a long-term cooperation practice based on three cooperation models. We shift from one model to another when this becomes good for the business, thus always providing you with the highest quality and optimal processes and costs.
We are dead on developing web apps, mobile apps, APIs, efficient data storage, and cloud hosting. At whatever stage of your SaaS project development (startup, post-MVP, launched product), you are faced with the need to cooperate with an outsourcing team, you will receive support and total immersion in your project.
Сonsider the IaaS
However, the SaaS model doesn’t suit every business and your business might need the highest level of control. Almost no company can do without an IT infrastructure - even a small company needs servers to store databases or tools that connect employees' computers into a common network.
A company can buy servers and set up this infrastructure on its own, but this is quite long and expensive. Or maybe not buy anything if you rent IaaS cloud services.
What the End-User Controls in IaaS
The IaaS provider furnishes infrastructure components, like servers, storage, and hardware for computing resources. The user is responsible for everything else, including purchasing, installing, configuring, and managing applications, websites, and operating systems.
Microsoft Azure and Google Compute are examples of IaaS. Compared to PaaS and SaaS, IaaS leaves a great deal of responsibility to the customer, which can be a drawback for some organizations. The advantages include managing the environment and customizing services to a larger degree.
What is the IaaS Option for Your Business?
The most obvious use for IaaS is moving away from physical servers and your IT infrastructure to the cloud. With IaaS, you can do everything with a physical data center - store data, set up a CRM system, deploy a website, or any business servers.
When is IaaS Being Utilized?
IaaS solutions are designed to be highly scalable and flexible, meaning you can buy additional resources and features you need as your operations expand. Compare this to having to buy more physical hardware and hiring more IT professionals for maintenance as your business grows and you require more storage and servers.
Saving on infrastructure
If you maintain the servers yourself, you must pay for premises, equipment, licensed software - large capital expenditures. In addition, in the cloud, the provider assumes the provision of virtual infrastructure with the downtime specified in the SLA (uptime). To provide the same uptime in your own private data center and manage physical infrastructure and virtualization, you need a separate staff of specialists. These are additional costs in excess of capital. In that case, the company needs to learn how to assess risks and additional and hidden costs, it needs to have the appropriate expertise, then it is cheaper to deploy IT infrastructure in the cloud.
Fast Business Startup
IaaS cloud infrastructure reduces business costs at the start, as it helps to reduce capital investments, and do without the purchase of equipment and the organization of a data center.
Infrastructure Expansion
Cloud IaaS technologies can also be used to extend existing infrastructure. For example, physical servers need to be more powerful for the current tasks. Instead of buying new ones, you can connect to the IaaS platform and get your needed power.
Infrastructure for Companies With Surges in Demand
IaaS is suitable if the company has a non-linear demand for resources. For example, you have physical servers running an online store. During the holidays or sales, the site falls - there are too many buyers, and the servers cannot stand it. If you use the cloud infrastructure, you can immediately get additional computing power as the load increases. And when the load drops, return to the planned capacity consumption. In the case of a conventional physical infrastructure, you need to buy additional servers - you will use them only at the peak of the load and serve constantly. This is not to mention the fact that the procurement process usually takes weeks, and cloud scaling - takes minutes or even seconds.
Development and Testing
As in your own on-premises infrastructure, in the cloud, you can organize separate development, testing, and "live" workload environments in which a ready-made application is running. But, unlike your own infrastructure, test environments can be deployed instantly in the cloud. After completing the tests, you can minimize unnecessary environments and not overpay for idle resources. All this simplifies and speeds up the software testing process and allows you to save money on the purchase of test servers.
Building a complex IaaS infrastructure in the cloud for large projects may require a provider's help with migration and administration. But for most projects, cloud infrastructure management does not require the direct involvement of the provider. And if difficulties arise, you can always contact technical support.
IaaS Advantages
The main advantage of IaaS for organizations is that it provides you with the greatest level of management and control over the infrastructure. IaaS is extremely scalable and considered the most flexible cloud computing model. The resources you need are offered as a service and can be purchased as needed or per consumption, often the basis for pricing as a pay-as-you-use model. Also, IaaS normally allows multiple users for a single piece of hardware.
IaaS Characteristics
-
Virtual servers (VPS / VDS) on which you can install various programs. Sometimes the provider offers servers immediately with operating systems so that you can quickly deploy the necessary applications to them.
-
Network settings allow virtual servers to communicate with each other, external servers owned by the client company and the Internet. These include:
- server availability for each other and the external network, routing of server network connections;
- load balancers that prevent server overloads by distributing incoming traffic between them;
- VPN is a technology for encrypting data transmitted by a company between the cloud and its physical data center;
-
User access control. For example, you can restrict access to individual virtual machines or allow viewing of data, prohibiting changing it.
-
Cloud storage is for storing files, data, or backups. They differ from ordinary cloud drives, which individual users deal with, with almost unlimited storage capacity and fast data access speed.
-
Backup and disaster recovery services ensure your infrastructure against falls and data loss when its individual nodes fail.
Examples of IaaS
There are several cloud infrastructure providers that you might be familiar with, such as DigitalOcean, Rackspace or Joyent.
One of the most popular is Google Compute Engine (GCE). The IaaS component of Google’s Cloud Platform is built on the global infrastructure that powers Google products and services. GCE enables you to operate high-performance and scalable virtual machines on demand, running on Google’s worldwide data centers and fiber network. It provides support for scaling from single instances to global cloud computing. There are no up-front costs; you just pay-as-you-go for the services you need, such as storage, data migration, networking, and management tools.
Consider the PaaS
Cloud service providers can provide pre-configured tools (platforms) for different tasks. The key difference between PaaS and IaaS is that here you have certain tools, for example, a database management system, machine learning or big data processing environment, and industrial IoT (IIoT). They must be customized to suit the company's needs but can be built from scratch. It saves developers time, for example, they do not need to fiddle with the development of the database, and they can load information into it and work.
What the End-User Controls in PaaS
At the same time, you do not have access to the operating system, the settings of virtual servers that underlie PaaS, as well as to the low-level settings of the platform itself. The ISP takes care of their optimal configuration and relieves you of the need to monitor settings, updates, scaling and security. You only get access to the interfaces of the platform itself.
What is the PaaS Option for Your Business?
PaaS gives you a cloud platform complete with components and a working framework upon which you can build custom applications. The required storage, server, network, runtime, middleware, virtualization, and OS are provided for and managed by the vendor while you get to maintain and control your apps and data. What is PaaS but much like SaaS as they both deliver service through the internet except that unlike delivering the software which SaaS does, PaaS instead delivers or makes available a platform for you to create your apps?
As such, it is the ideal service for developers who don’t have to worry about infrastructure, servers, data storage, operating systems, and other special components that are built into the service. Imagine starting from scratch and purchasing all the components you need to write extensive code and create custom apps. These will require a lot of your time aside from a hefty investment.
When is PaaS Being Utilized?
Database
All or part of the company's databases can be transferred to the cloud. In the case of IaaS, the user only gets disk space and must choose the database management system, install and configure it, and provide data protection and backup. In PaaS, the DBMS is already installed, you just need to configure it for yourself and load the data. The provider is responsible for the performance and backup.
Developing applications in containers
This is the modern standard for application development. The bottom line is that all the components needed to run the application are packaged in separate virtual containers. You can quickly invoke them, launch applications, and add computational power to scale quickly and withstand high loads.
Big data analytics
PaaS helps to process historical big data, that is, arrays of information collected by a company over time, and data in real-time. To do this, use tools such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka and others. They are already installed and configured in the cloud, you just have to choose the desired configuration.
Machine learning
Such a platform as a service allows you to quickly develop applications based on deep learning for the company's needs: computer vision systems for recognizing faces, license plates, and audio analytics systems. For example, you have a large database of employee photographs, and you want to set up barrier-free entry at the facility - letting employees pass through the turnstiles and recognize their faces. To do this, you develop your own application and then "teach" the neural network to recognize employees using PaaS, where facial recognition tools are already installed.

PaaS services save time configuring the infrastructure your company needs. You can connect the required set of services. The main thing is to ensure that the cloud provider has the solutions you need now and in the future.
PaaS Advantages
PaaS lets developers concentrate on the task at hand – creating unique and custom apps and testing and deploying them – without being bogged down with peripheral matters like security patches and updates. It is designed around virtualization technology and built to be easy and simple to use, even for those without a background in systems administration. PaaS is also quite scalable, allowing you to pick from different tiers of components and resources you need to match the scope of your project. All these make PaaS a time and cost-saving cloud computing solution.
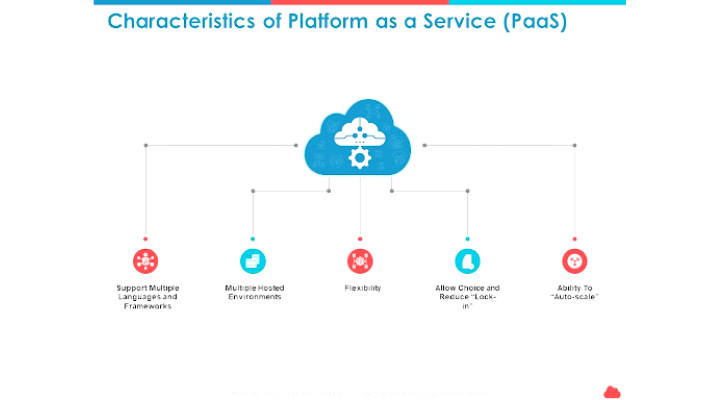
PaaS Characteristics
Examples of PaaS
Some PaaS examples are widely used, such as Microsoft Azure, OpenShift, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, or Heroku.
Sometimes, experts also prefer Google App Engine. Part of Google’s range of cloud services, this PaaS solution is for web app developers and companies with access to Google’s scalable hosting and tier 1 internet service. GAE requires that apps be written in Python or Java and utilize Google’s query language. For usage of resources up to a certain amount, GAE is free. You start paying when you exceed the per-minute or per-day usage rate of storage, CPU, and other resources.
We Can Conclude the Cloud Solutions Increase Efficiency
The market for cloud services is growing, and companies' spending on cloud services has already crossed the $ 1 billion mark. The high demand is associated with the new opportunities clouds are opening up to the business. In 2023, there will be more such opportunities: companies that choose cloud infrastructure can significantly save on IT and bring products to market faster.
In the long term, moving to the cloud platform will enable companies to outrun the competition and respond more quickly to changing market needs. With clouds, businesses can focus on strategic tasks without being distracted by the administration and maintenance of the IT infrastructure.
Are you ready for cloud migration and looking to hire a dedicated software development team to handle this? Let’s have a call with our cloud experts, that will help with this business transformation.